The Complete Guide to Lung Operation Procedures
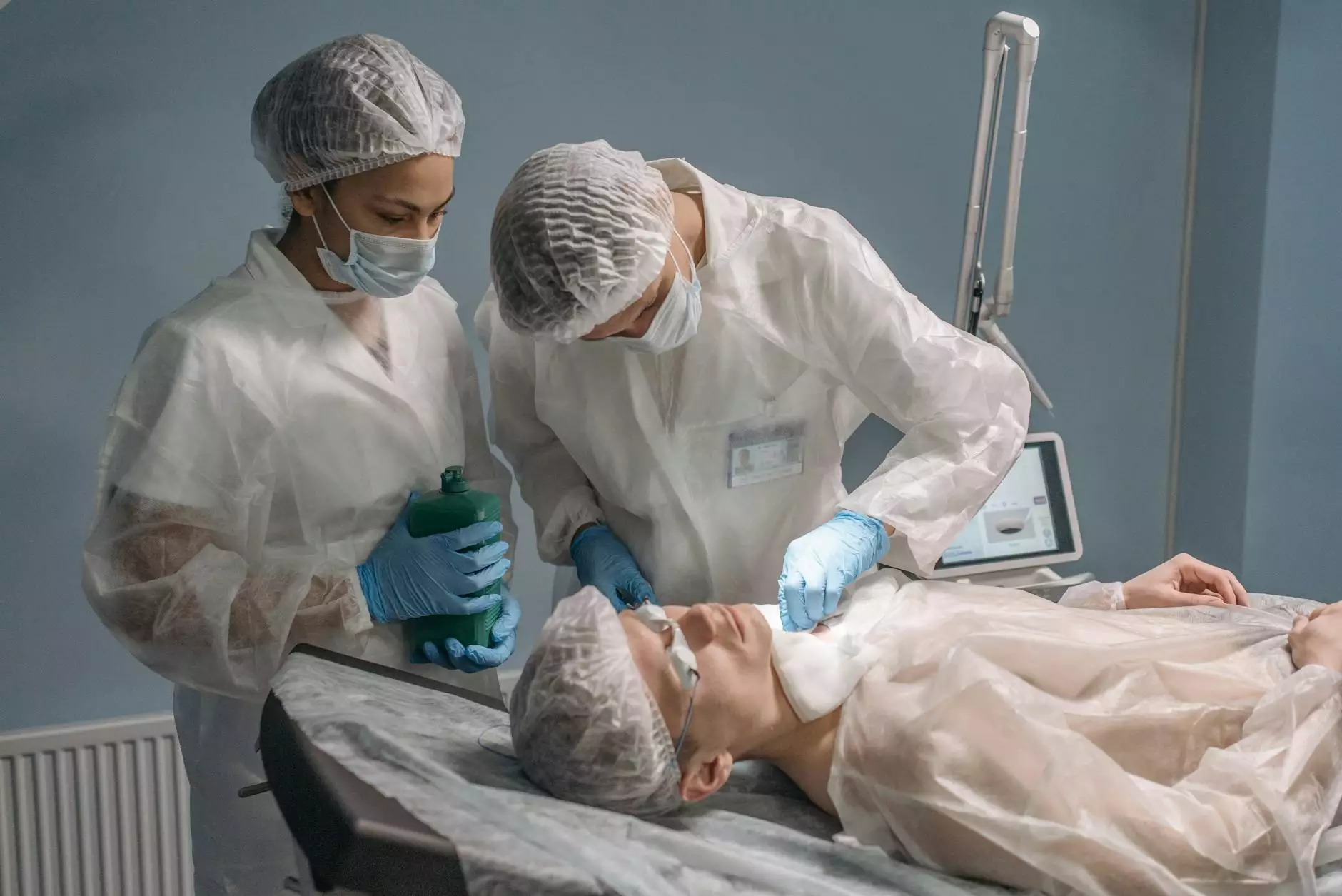
Understanding lung operation procedures is crucial for patients facing respiratory issues that require surgical intervention. This comprehensive guide provides detailed information about the different types of lung surgeries, preparation, recovery, and what to expect throughout the process. Join us at Neumark Surgery as we delve into the intricacies of lung operation procedures.
What is a Lung Operation Procedure?
A lung operation procedure refers to various surgical techniques aimed at treating conditions affecting the lungs. These procedures can vary significantly in complexity and purpose, ranging from minimally invasive techniques to major surgeries. The primary goal is to enhance lung function, remove tumors, or address serious respiratory issues.
Types of Lung Operation Procedures
There are several types of lung surgeries, each tailored to specific conditions:
- Lobectomy: Removal of one lobe of the lung, commonly performed for lung cancer.
- Pneumonectomy: Complete removal of a lung, usually due to extensive disease.
- Sleeve Resection: Removal of a part of the bronchus along with the tumor.
- Segmentectomy: Removal of a segment of the lung, typically for localized tumors.
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): A minimally invasive procedure using small incisions to perform lung surgeries.
- Thoracotomy: An open surgical approach to access the lung, often used for extensive surgeries.
Indications for Lung Surgery
Lung operation procedures are recommended for various medical conditions, including but not limited to:
- Lung Cancer: The most common reason for lung surgeries, aimed at removing cancerous tissues.
- Infections: Severe cases of pneumonia or tuberculosis that do not respond to medication may require surgical intervention.
- Interstitial Lung Disease: Conditions leading to progressive lung scarring.
- Collapsed Lung (Pneumothorax): In some cases, surgical repair is necessary.
- Emphysema: In severe cases, lung volume reduction surgery may be indicated.
The Lung Operation Procedure: An Overview
Before the Procedure
Prior to undergoing a lung operation procedure, patients must prepare adequately. This includes:
- Medical Evaluation: A thorough assessment by the surgical team, including imaging studies like X-rays or CT scans.
- Pulmonary Function Tests: To assess lung capacity and function.
- Cardiac Evaluation: Ensuring the heart is healthy enough for surgery.
- Smoking Cessation: Patients are strongly advised to stop smoking before surgery to enhance recovery.
- Medication Management: Patients should discuss all medications with their surgeon, including blood thinners and supplements.
During the Procedure
The surgical process can vary depending on the type of lung operation being performed. In general, the steps include:
- Anesthesia: Patients will be given general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free.
- Incision: Based on the type of surgery, the surgeon will make an incision in the chest, which may be small for minimally invasive methods or larger for open surgery.
- Accessing the Lung: The surgeon will carefully navigate through the ribs or the chest wall to reach the lungs.
- Performing the Surgery: The specific procedure will be carried out, be it resection of a tumor or complete lobe removal.
- Closure: Once the procedure is complete, the surgeon will close the incision using sutures or staples.
Post-Operative Care
After a lung operation procedure, the focus shifts to recovery. Key aspects of post-operative care include:
- Monitoring: Patients will be monitored in a recovery area for signs of complications.
- Pain Management: Effective pain management strategies will be implemented, including medications.
- Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises are often encouraged to prevent complications like pneumonia.
- Gradual Mobility: Patients are encouraged to begin moving as soon as possible to enhance recovery.
Managing Recovery After Lung Surgery
Recovery after a lung operation procedure is a critical phase that should not be overlooked. Patients can expect:
- Hospital Stay: Depending on the surgery type, hospitalization may range from a few days to a week.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up visits to the surgeon to monitor healing and pulmonary function will be essential.
- Respiratory Therapy: Some patients may need sessions with a respiratory therapist to aid in lung function recovery.
- Return to Activities: Activity level restrictions should be followed, with a gradual return to normal activities over weeks.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like all surgical procedures, lung operations come with potential risks and complications, including:
- Infection: Post-operative infections at the site of surgery or within the lungs are possible.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery could require further intervention.
- Pneumothorax: Air leaks into the chest cavity might occur, especially after lung surgery.
- Respiratory Issues: Patients may experience difficulties in breathing post-surgery.
- Blood Clots: This could happen in the legs or lung, leading to serious complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the lung operation procedure is vital for those facing lung health concerns. With various surgical techniques available, comprehensive pre-operative evaluation, and diligent post-operative care, patients can navigate their recovery journey effectively. At Neumark Surgery, we are dedicated to providing expert care for our patients, ensuring they have the support and knowledge needed throughout the entire process.
For more information about lung surgeries or to schedule a consultation, please visit neumarksurgery.com.